FAQs¶
This page lists some frequently asked questions that may arise in container management, providing you convenience to perform troubleshooting.
-
Helm application installation failed with "OOMKilled" error message

As shown in the figure, the container management module will automatically create and launch a Job responsible for installing the specific application. In version v0.6.0, due to unreasonable job resource settings, OOM was caused, affecting application installation. This bug has been fixed in version 0.6.1. If you upgrade to the environment of v0.6.1, it will only take effect in new created or accessed clusters. Existing clusters need to be manually adjusted to take effect.
Click to check how to adjust script
- The following scripts are executed in the global service cluster
- Find the corresponding cluster, take skoala-dev as an example in this article, and obtain the corresponding skoala-dev-setting configmap.
-
After updating the configmap, it will take effect.
kubectl get cm -n kpanda-system skoala-dev-setting -o yaml apiVersion: v1 data: clusterSetting: '{"plugins":[{"name":1,"intelligent_detection":true},{"name":2,"enabled":true,"intelligent_detection":true},{"name":3},{"name":6,"intelligent_detection":true},{"name":7,"intelligent_detection":true},{"name":8,"intelligent_detection":true},{"name":9,"intelligent_detection":true}],"network":[{"name":4,"enabled":true,"intelligent_detection":true},{"name":5,"intelligent_detection":true},{"name":10},{"name":11}],"addon_setting":{"helm_operation_history_limit":100,"helm_repo_refresh_interval":600,"helm_operation_base_image":"release-ci.daocloud.io/kpanda/kpanda-shell:v0.0.6","helm_operation_job_template_resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"50m","memory":"120Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"50m","memory":"120Mi"}}},"clusterlcm_setting":{"enable_deletion_protection":true},"etcd_backup_restore_setting":{"base_image":"release.daocloud.io/kpanda/etcdbrctl:v0.22.0"}}' kind: ConfigMap metadata: labels: kpanda.io/cluster-plugins: "" name: skoala-dev-setting namespace: kpanda-system ownerReferences: - apiVersion: cluster.kpanda.io/v1alpha1 blockOwnerDeletion: true controller: true kind: Cluster name: skoala-dev uid: f916e461-8b6d-47e4-906e-5e807bfe63d4 uid: 8a25dfa9-ef32-46b4-bc36-b37b775a9632Modify
clusterSetting->helm_operation_job_template_resourcesto the appropriate value, and the value corresponding to version v0.6.1 iscpu: 100m,memory: 400Mi.
-
Permission issues between the container management module and the global management module
Users often ask why they can see a particular cluster or why they cannot see a specific cluster. How can we troubleshoot related permission issues? The permissions in the container management module are divided into cluster permissions and namespace permissions. If a user is bound, they can view the corresponding cluster and resources. For specific permission details, refer to the Cluster Permission Explanation.

In the global management module, user authorization includes using the admin account, going to Global Management -> Users and Access Control -> Users menu, finding the corresponding user. In the Authorize User Group tab, if there are roles such as Admin, Kpanda Owner, etc., that have container management permissions, even if the cluster permissions or namespace permissions are not bound in the container management, they can see all clusters. For more information, refer to User Authorization Documentation

In the global management module, workspace binding involves using the account to go to Global Management -> Workspaces and Hierarchies, where you can see your authorized workspace. Click on the workspace name.
-
If the workspace is authorized for you individually, you can see your account in the authorization tab, then check the resource group or shared resource tab. If the resource group is bound to a namespace or the shared resource is bound to a cluster, then your account can see the corresponding cluster.
-
If you have been granted a global management-related role, you will not see your account in the authorization tab, and you will not be able to see the cluster resources bound to the workspace in the container management module.

-
-
When installing applications with Helm, unable to pull the kpanda-shell image
After offline installation, connected clusters often encounter failures in pulling the kpanda-shell image, as shown in the image:

In this case, simply go to the cluster management - cluster settings page, advanced configuration tab, and modify the Helm base image to a kpanda-shell image that can be successfully pulled by the cluster.

-
Helm Chart interface does not display the latest Chart uploaded to the corresponding Helm Repo, as shown in the image:

In this case, simply refresh the corresponding Helm repository.

-
When an application installation with Helm fails and is stuck in installation, unable to delete the application for reinstallation, as shown in the image:

In this case, simply go to the custom resources page, find the helmreleases.helm.kpanda.io CRD, and then delete the corresponding helmreleases CR.


-
After removing node affinity and other scheduling strategies in Workloads, abnormal scheduling occurs, as shown in the image:

In this case, it may be due to the incomplete removal of the strategy. Click on edit and delete all strategies.



-
What is the logic behind Kcoral checking the Velero status of a working cluster?

- The working cluster has installed standard Velero components in the velero namespace.
- The velero control plane, specifically the velero deployment, is in a running state and meets the expected replica count.
- The velero data plane, specifically the node agent, is in a running state and meets the expected replica count.
- Velero successfully connects to the target MinIO (BSL status is Available).
-
When performing cross-cluster backup and restore with Kcoral, how does it determine the available clusters?
When performing cross-cluster backup and restore applications with Kcoral, in the restore page, Kcoral will help filter the list of clusters capable of performing cross-cluster restore based on the following logic:

- Filtering out clusters that have not installed Velero.
- Filtering out clusters with abnormal Velero status.
- Obtaining a list of clusters that are connected to the same MinIO and Bucket as the target cluster and returning them.
Therefore, as long as the clusters are connected to the same MinIO and Bucket, and Velero is in a running state, cross-cluster backup (requires write permission) and restore can be performed.
-
After uninstalling VPA, HPA, CronHPA, why do the corresponding elastic scaling records still exist?
Even though the components were uninstalled through the Helm Addon market, the related records in the application elastic scaling interface remain, as shown in the image:

This is a problem with helm uninstall, as it does not uninstall the corresponding CRD, causing residual data. In this case, we need to manually uninstall the corresponding CRD to complete the final cleanup.
-
Why does the console fail to open on clusters with lower versions?
In Kubernetes clusters with lower versions (below v1.18), opening the console results in a CSR resource request failure. When opening the console, the current logged-in user in the target cluster requests a certificate through the CSR resource. If the cluster version is too low or this functionality is not enabled in the controller, the certificate request fails, preventing connection to the target cluster.
Refer to the certificate request process.
Solution:
-
If the cluster version is greater than v1.18, check if kube-controller-manager has enabled the csr feature, ensuring the following controllers are normal:
-
The only solution for lower version clusters is to upgrade the version.
-
-
How to reset a created cluster?
Created clusters fall into two categories:
- Clusters that failed to create: Clusters that failed to create due to parameter errors during the creation process can be retried by selecting retry on the failed installation and then reconfiguring the parameters for a new creation.
- Successfully created clusters: These clusters can be uninstalled first, and then recreated. Uninstalling a cluster requires disabling cluster protection to uninstall the cluster.


-
Failure to install plugins when connecting to a cluster
In offline environments connected clusters, before installing plugins, you need to configure the CRI proxy repository to ignore TLS verification (needs to be executed on all nodes).
-
Modify the file
/etc/docker/daemon.json -
Add "insecure-registries": ["172.30.120.243","temp-registry.daocloud.io"], to the content after modification:
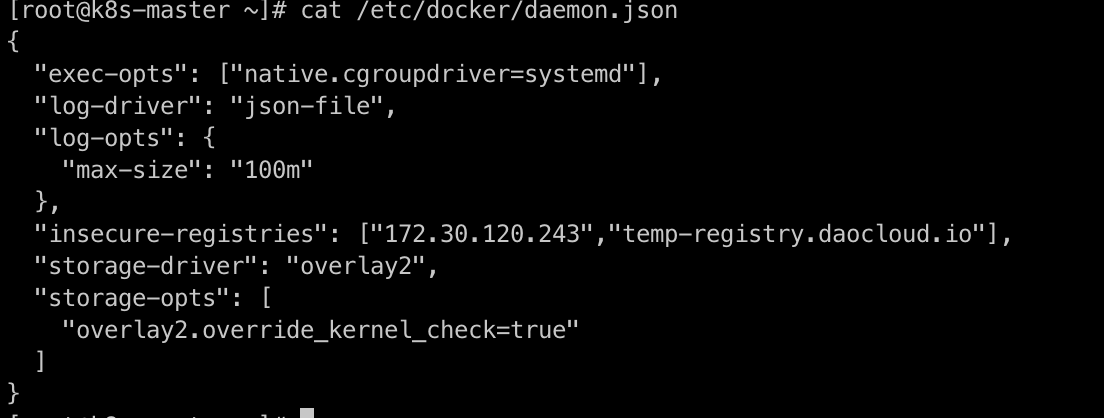
-
Restart docker
-
Modify
/etc/containerd/config.toml -
After modification, the content should be as follows:
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors."docker.io"] endpoint = ["https://registry-1.docker.io"] [plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors."temp-registry.daocloud.io"] endpoint = ["http://temp-registry.daocloud.io"] [plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.configs."http://temp-registry.daocloud.io".tls] insecure_skip_verify = true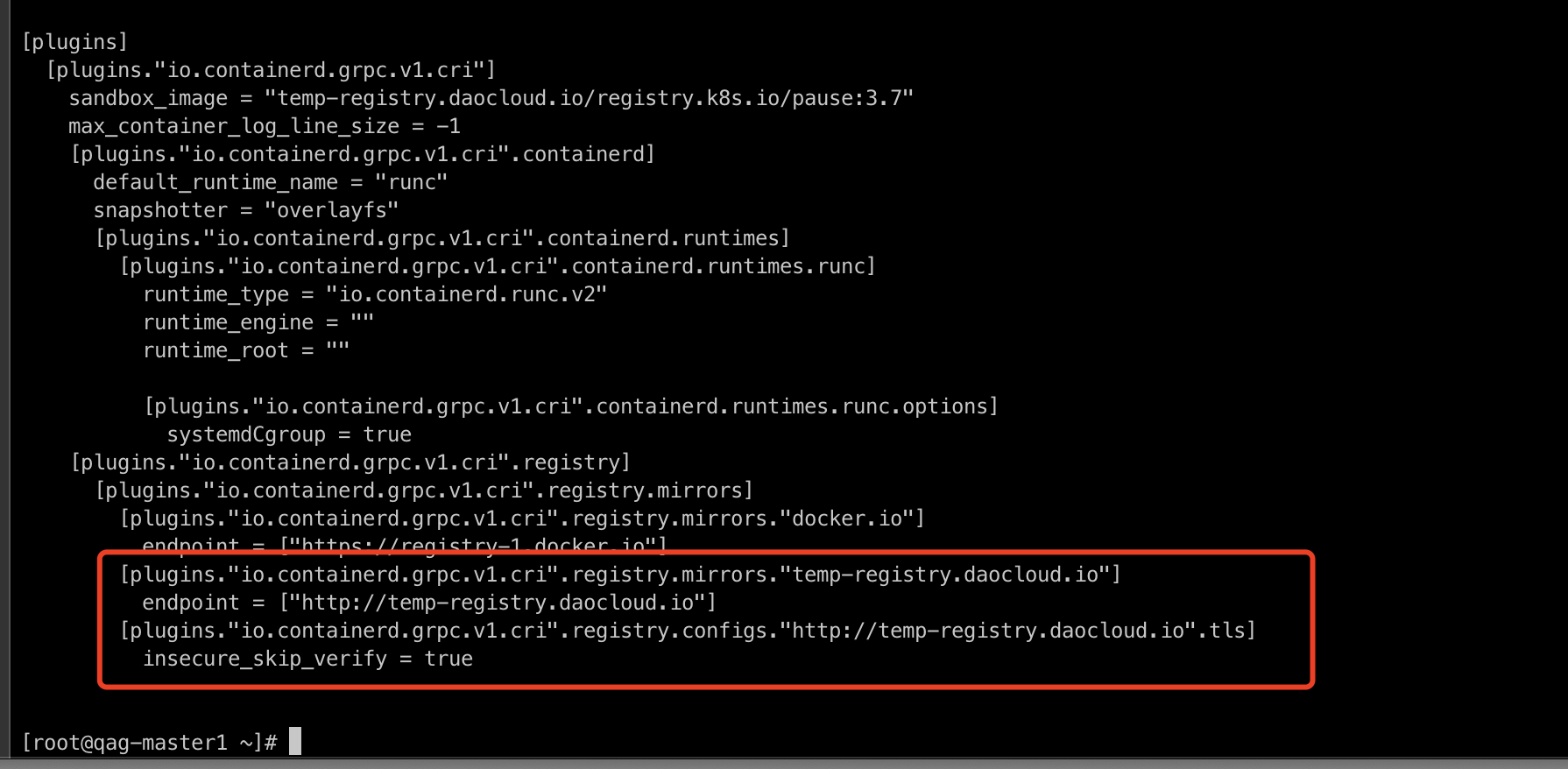
-
Pay attention to spaces and line breaks, ensure the configuration is correct, and after modification, execute:
-
-
When creating a cluster, enabling Kernel Tuning for New Clusters in advanced settings causes cluster creation failure.
-
Check if the conntrack kernel module is loaded by running the following command:
-
If it returns empty, it means it is not loaded. Reload it by running the following command:
Note
Upgrading the kernel module can also cause cluster creation failures.
-